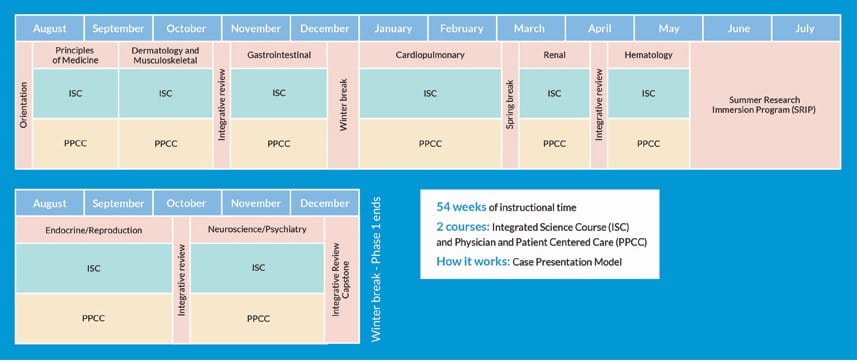
Phase 1: Principles of Medical Science and Practice
Phase 1 of Geisinger Commonwealth’s MD Program incorporates foundational science and clinical education from day one of medical school.
After a comprehensive transition to medical school program, you'll be enrolled in two courses, the Integrated Science Course (ISC) and the Physician and Patient Centered Care Course (PPCC). These courses are delivered as integrated organ-system blocks, separated from one another by integrative review weeks designed to bring together the knowledge and skills mastered during the preceding weeks of the curriculum.
Additionally, you'll have dedicated time over the summer to participate in the Summer Research Immersion Program.
The phase ends with an Integrative Review Capstone (IRC) course, which includes complex patient encounters and challenging multisystem diagnostic problems which let you integrate previously acquired knowledge, including the complexities of the social determinants of health, healthcare disparities and how a patient interacts with a health system.